| FORCES & MOTION |
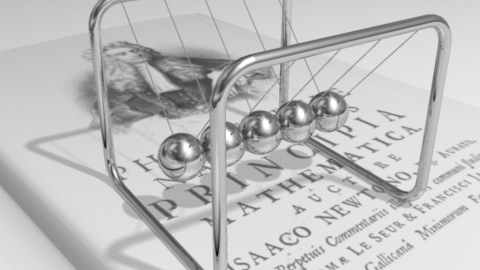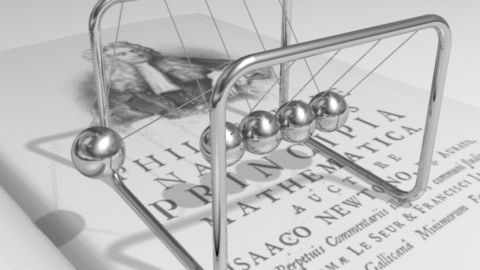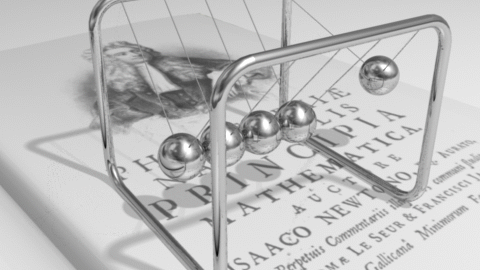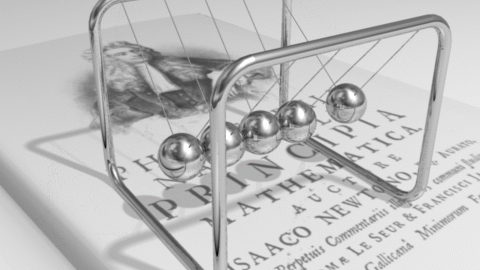
Image from www.bioedonline.org
|
 Image from www.bioedonline.org |
|
Sir Isaac Newton was one of the greatest scientists and mathematicians that ever lived. Newton had new ideas about motion, which he called his three laws of motion. He also had ideas about gravity, the diffraction of light, and forces. According to Newton's first law, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is often called "the law of inertia". This means that there is a natural tendency of objects to keep on doing what they're doing. All objects resist changes in their state of motion. In the absence of an unbalanced force, an object in motion will maintain this state of motion. According to Newton's second law, Acceleration is produced when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass (of the object being accelerated) the greater the amount of force needed (to accelerate the object). Everyone unconsiously knows the Second Law. Everyone knows that heavier objects require more force to move the same distance as lighter objects. However, the Second Law gives us an exact relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. It can be expressed as a mathematical equation: F = MA According to Newton's third law, for every action there is an equal and opposite re-action. This means that for every force there is a reaction force that is equal in size, but opposite in direction. That is to say that whenever an object pushes another object it gets pushed back in the opposite direction equally hard. Activity 1: The Inclined Plane We are going to watch a video segment from The Big Bang Theory (1x02) where its main characters have “a little problem” with an inclined plane, force and motion. After watching it, answer these questions: a) Sheldom claims that it is exactly the half to go up the box through the inclined plane. Is it right? Why or why not? b) If it were a ramp instead of the stairs, would the effort change? c) If we had a null friction, would Sheldon’s assertion “exactly the half” be true? Activity 2: Vocabulary We need to understand the new concepts related to this unit; then, we are going to see the different flashcards, improving our pronunciation. Activity 3: Newton’s Laws Now, we are ready to learn about the three Newton’s Laws of motion. In this activity we will develop an understanding of each of Newton's Three Laws of Motion. Firstly, we are going to watch the video from Khan Academy where these three Laws are explained. Then, in groups, you must look for more information about them, complete the mind-map and make a power-point presentation about them in Prezi. Then, it will be presented to the rest of the class. Activity 4: Simulations In pairs, you must do all the possibilities from the simulations in the activity. Take notes, and answer the questions from the teacher. Activity 5: Quiz We have learnt all related to forces and motion, now you must prove what you know about this topic. Final Task: In groups, you must make a video where you demonstrate the different concepts learnt in this unit: force, motion, weight, mass, position, inertia, gravity, friction, reference object, balanced and unbalaced force… Then, you will upload it to Moodle and present it to the rest of the class. |
Links: |